Addiction
Table of Contents
- What Is the Reason for Using Tests to Detect Drug Use?
- How Long Does It Take Your Body to Eliminate Drugs?
- How Does the Body Eliminate Drugs?
- How Are Drugs Detected in the Body?
- How Long Do Drugs Stay Detectable in Your System by Category?
- What Factors Affect Drug Detection Times?
- What Causes Drugs to Remain in the Body Longer Than Their Predicted Elimination Half-Lives?
- Can Narcan (Naloxone) Reduce the Elimination Half-Life of an Opioid?
- Are At-Home Drug Tests as Effective as Lab Tests?
- How Do People Try to Beat Drug Tests?
- Can Detox Remove Drugs From the System Faster?
- What to Do if I Can’t Pass a Drug Screening?
- Finding Help for a Drug Addiction
Key Points
- Attempts to “beat” a drug test are detectable.
- A drug stays in your system for four to five times its elimination half-life.
- Certain factors like age, preexisting medical conditions, and metabolism can affect a drug’s elimination half-life.
- Diluting urine will not remove drug metabolites from your system, although it may be undetectable in the urine.
- Metabolites are detectable longer than the primary drug in most cases.
- Once the body breaks down a drug (metabolized), byproducts (metabolites) remain for a specified time.
What Is the Reason for Using Tests to Detect Drug Use?
According to the American Society for Addiction Medicine (ASAM), drug testing should be used to discourage nonmedical drug use and to divert individuals from using controlled substances. [1] Additional reasons include:- Determining treatment in emergencies where a person is unable to communicate
- Encouraging entry into addiction treatment
- Identifying early relapse
- Improving outcomes of addiction treatment through long-term monitoring
- Determining someone’s ability to complete hazardous tasks safely
- Assessing a person’s mental health and mental health condition
- Fulfilling the Department of Transportation (DOT)’s federally mandated requirement to test private-sector transportation workers
How Long Does It Take Your Body to Eliminate Drugs?
Up to 97% of a drug will remain in your system for four to five elimination half-lives.[2] Each drug has its own elimination half-life, which depends on the users’ metabolism, state of health, age, and route of administration.Drug Elimination Half-Lives of Commonly Tested Drugs
The elimination half-life of the most commonly used drug classes are:- Stimulants:[3] Nine hours for short-acting stimulants and nine to 13 hours for long-acting stimulants.
- Benzodiazepines:[4] Short-acting benzodiazepines have an elimination half-life ranging from one to 12 hours. Intermediate benzodiazepines have an elimination half-life of 12 to 40 hours. Long-acting benzodiazepines have an elimination half-life that varies between 40 and 250 hours.
- Opioids:[5] Ultra-short opioids have an elimination half-life of 0.6 hours, and ultra-long-acting opioids have an elimination half-life of 24 to 36 hours.
- Cannabinoids:[6] THC, the active compound in cannabis, has an elimination half-life of one to three days in casual users. The drug stays in the system for five to 13 days in chronic users.
- Alcohol:[7] The elimination half-life of alcohol is four to five hours. However, according to the Cleveland Clinic, this amount depends on how much the person drinks and how often they drink.[7]
How Does the Body Eliminate Drugs?
According to the Merck Manuals, most drugs are water-soluble and are processed by the kidneys and bladder.[8] These drugs and their metabolites are then excreted through urination. In contrast, fat-soluble drugs are processed by the liver and excreted in bile. Other methods of elimination include sweat, saliva, respiration, and breast milk.How Are Drugs Detected in the Body?
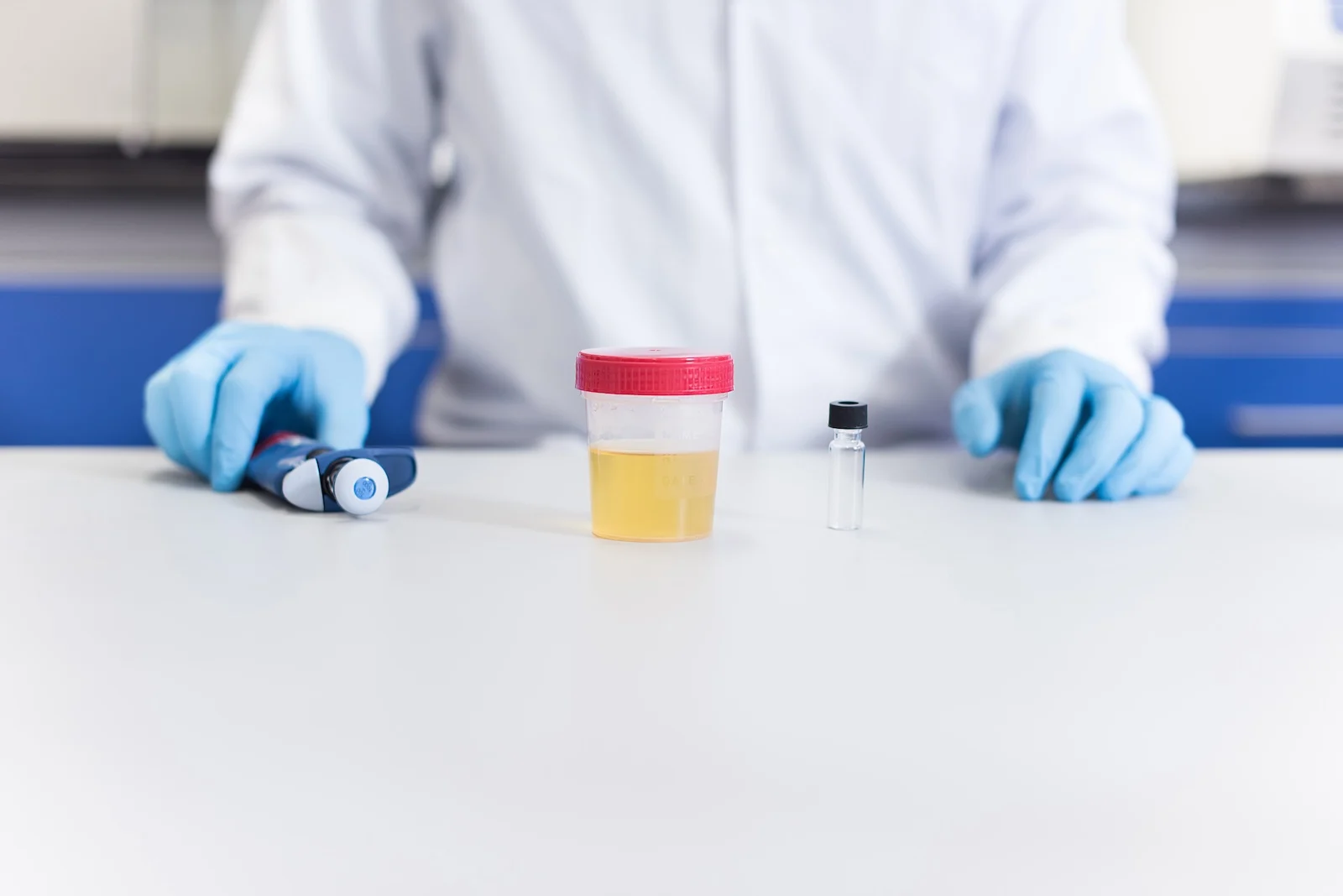 Although urine, blood, saliva, and hair are the most commonly tested matrices, it is possible to detect drugs in sweat, breath, and meconium. The latter is useful in determining whether a mother-to-be has engaged in drug use during pregnancy, though the collection window is narrow. [1]
Although urine, blood, saliva, and hair are the most commonly tested matrices, it is possible to detect drugs in sweat, breath, and meconium. The latter is useful in determining whether a mother-to-be has engaged in drug use during pregnancy, though the collection window is narrow. [1]
Urine Analysis
Urine drug tests are commonly used, and there are numerous advantages to choosing them.[1] They include:- Detecting higher concentrations of drugs and their metabolites
- Offering a greater availability of point-of-care tests (POCTs)
- A short window of detection
- Samples that are easy to adulterate
- Samples that are easy to substitute
Blood Analysis
Blood collection requires professional administration and collection, so it isn’t usually the first testing method for drugs or their metabolites; however, the results are harder to adulterate and incredibly accurate. The disadvantages of blood testing include:[1]- A limited window of detection
- A higher risk of infection
- A more invasive collection method
Hair Analysis
Hair collection is a commonly used non-invasive collection method. It offers the most extended detection window of all the collection methods. Other advantages include: [1]- Observed collection
- Detects changes in drug use over time
- Easy storage and transport
- Harder to adulterate
- Readily available sample
- Cost and time
- Cannot detect drug use within the past 10 days
- Only select laboratories process hair detection tests
- Darker hair color holds more of the drug
- Environmental contamination is a possibility
- Shaving removes the specimen
Saliva Analysis
Saliva (oral fluid) is a relatively easy matrix to test for drugs and their metabolites. The advantages of using saliva over other matrices include reduced risk of adulteration, same-day collection in most cases, and the ability to detect residual drugs. The disadvantages of using saliva tests, however, are numerous and include:[1]- Short window of testing
- Saliva can be adulterated by stimulant use
- Limited specimen volume
- Contamination from residual drugs
- Requires supervision of patient before sampling
How Long Do Drugs Stay Detectable in Your System by Category?
The following detection times are divided by category and testing method. [1]Alcohol
Alcohol is a central nervous system depressant that causes users to feel relaxed and euphoric. Examples of alcohol are beer, wine, and champagne.[10] Detection times based on the testing method are:- Urine: 10 to 12 hours
- Hair: Not applicable
- Saliva: 24 hours
Amphetamines
Adderall is a well-known prescription amphetamine used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and narcolepsy.[11] Adderall and similar drugs stay in the system for:- Urine: two to four days
- Hair: up to 90 days
- Saliva: one to 48 hours
Methamphetamines
Desoxyn is an example of a prescribed methamphetamine used to treat ADHD. Crystal meth is an example of an illegal methamphetamine.[12] They are detectable in the system for:- Urine: two to five days
- Hair: up to 90 days
- Saliva: one to 48 hours
Barbiturates
Barbiturates are a class of drugs used to treat insomnia and seizures.[13] Barbiturates are detectable in the system for:- Urine: up to seven days
- Hair: up to 90 days
- Saliva: not applicable
Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines such as lorazepam (Ativan) and diazepam (Valium) are prescribed to people with anxiety disorders and panic disorders.[14] They are detectable in the system for- Urine: up to seven days
- Hair: up to 90 days
- Saliva: not applicable
Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids such as hashish and marijuana contain the active ingredient THC.[15] It is detectable in the system for:- Urine: one to 30 days
- Hair: up to 90 days
- Saliva: 24 hours
Cocaine
Cocaine is an illegal stimulant that elicits hallucinations and speeds up activity in the brain.[16] It is detectable in the system for:- Urine: one to three days
- Hair: up to 90 days
- Saliva: one to 36 hours
Codeine
Codeine is a well-known painkiller that has addictive properties.[17] Although it is useful in treating severe, acute pain, the benefits may outweigh the risks in individuals with substance use disorder. Codeine is detectable in the system for:- Urine: two to four days
- Hair: up to 90 days
- Saliva: one to 36 hours
Morphine
Morphine is often used to treat pain as a result of burns, gunshots, and broken bones. It is often provided intravenously in a hospital setting.[18] The detection times for morphine include the following:- Urine: two to five days
- Hair: up to 90 days
- Saliva: one to 36 hours
Heroin
Heroin is an illegal opioid abused for its euphoric effects.[19] It is detectable in the system for:- Urine: two to three days
- Hair: up to 90 days
- Saliva: one to 36 hours
Phencyclidine (PCP)
Phencyclidine (PCP), also known as angel dust, is a dissociative anesthetic that produces audible and visual hallucinations in the user as well as a sense of euphoria.[20] Phencyclidine detection times are:- Urine: five to six days
- Hair: up to 90 days
- Saliva: not applicable
What Factors Affect Drug Detection Times?
According to the National Library of Medicine, drug detection times depend on many factors including, but not limited to:[9]- Dose
- Duration of use
- Route of administration
- pH concentration of the matrix tested
- Variations in metabolic and renal clearance
What Causes Drugs to Remain in the Body Longer Than Their Predicted Elimination Half-Lives?
Certain factors can affect the timeframe for drug elimination. For example, some medications can interact with one another, leading to an increased concentration of the drug in the system and influencing its elimination rate. Additionally, specific detoxifying agents may shorten the time it takes for a drug to be cleared from the body.Can Narcan (Naloxone) Reduce the Elimination Half-Life of an Opioid?
Naloxone is a medication that reverses the effects of an opioid overdose. Some may believe that it reduces the elimination half-life of opioids like fentanyl or oxycodone, but according to Stat Pearls, a subsidiary of the National Library of Medicine, Naloxone blocks and reverses the effects of opioids without changing their elimination half-life.[21] This means that it is possible for someone to experience a second overdose if they use opioids soon after receiving Naloxone. Note: Intranasal Narcan has an elimination half-life of 1.85 to 2.08 hours in healthy individuals, whereas intramuscular Narcan has an elimination half-life of 1.24 hours.[21]Are At-Home Drug Tests as Effective as Lab Tests?
Advancements in science have resulted in the development of at-home drug tests that can be as accurate as those conducted in laboratory settings. However, before relying on the results of an at-home drug test, it is important to consider the following factors:- At-home drug tests can be easily contaminated, leading to false positives or negatives.
- At-home drug tests can be manipulated.
- Administering the test incorrectly can result in a false positive or negative.
- At-home drug tests detect the presence of drugs in the urine, which can be diluted to beat the test.
How Do People Try to Beat Drug Tests?
In an attempt to subvert a drug test, people may follow specific methods to dilute the testing medium. According to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), drug test subversion products include those that strip the hair, dilute the urine, and alter metabolites in blood samples.[23] These products are sought online and purchased from companies that do not perform testing on them. This makes them dangerous to use and, in many cases, illegal. It’s important to note that some drug test laboratories have methods for detecting the use of certain products. If a person is found using one of these products, they may have to retake the test, or it could be noted that they attempted to tamper with the sample.Can Detox Remove Drugs From the System Faster?
Detoxification is a natural process performed by your kidneys and liver to remove drugs from your system.[24] However, there are drug detox programs that offer medications to help individuals in their recovery from addictive substances.[25] These medications are not designed to accelerate the elimination of the addictive substance, but they are effective at reducing drug cravings and alleviating withdrawal symptoms. Furthermore, there is no science behind the claims that drinking apple cider vinegar or water or taking activated charcoal can detox drugs from the body within 24 hours.[23]What to Do if I Can’t Pass a Drug Screening?
If you consistently fail drug tests, it may indicate that you have a substance use disorder. Individuals with substance use disorder (SUD) find it difficult to stop using addictive substances because these substances create chemical changes in the brain, leading to dependence.[26] Dependence causes cravings and symptoms that make it difficult to stop using. This is caused by motivational centers in the brain, like the extended amygdala, prompting you to seek more of the drug so it can reward you with dopamine.[27] Additionally, people with SUD may develop a tolerance, meaning they need to consume more of the substance to experience its original effects. If you’ve tried to stop using drugs but relapsed, continued using drugs despite adverse consequences, or experienced withdrawal symptoms that make it hard for you to abstain, you may have SUD.[28] People with SUD may fail several drug tests or try to find methods to subvert them. Unfortunately, when a substance use disorder goes untreated, the condition rarely gets better and may worsen, becoming a full-blown addiction.Finding Help for a Drug Addiction
It’s important to recognize that substance use disorders (SUD) are not a matter of personal choice; they are brain disorders that make it difficult for individuals to stop using drugs, even when they want to. If you’re feeling alone in this struggle, remember that help is available, and reaching out for support is crucial. Evidence-based programs, such as 12-step meetings, medication-assisted treatment, and psychotherapy, have been proven effective in helping people with SUD achieve lasting recovery. These programs are often provided at rehabilitation centers or drug treatment facilities, where you can find the support necessary to overcome addiction and regain control of your life. To learn more about these programs and the many options available to assist you on your road to recovery, please contact Southeast Addiction Center TN. Our team of experts is ready to answer any questions you may have about substance use disorder treatment programs and help you choose the right program for your needs. You’ve already taken the first step; let us help you on the rest of your journey.Frequently Asked Questions
Why are drugs detectable in the urine for longer periods than in the blood?
More drugs enter the urine than their metabolites, which are more concentrated in urine samples.
Why do some drug testing centers use hair instead of urine?
Hair is a more challenging test medium to manipulate than urine or blood. Therefore, some laboratories prefer hair testing, though it is more expensive to administer than a urine test.
What are metabolites, and why do they remain after the drug has gone?
Metabolites are drug byproducts. When the liver metabolizes a drug, it is converted from its toxic form to a non-toxic form for elimination. This is why metabolites often remain in the blood, urine, saliva, and hair long after the drug itself has been processed.
There is a Better Way to Live. It's Time to Get the Help You Deserve.
Take the first step in getting your life back. Speak with our admissions team today.Sources
[1]National Library of Medicine. (207 Jul 1) Objective Testing – Urine and Other Drug Tests. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4920965/ on 2025 Feb 14.
[2] National Library of Medicine. (2023 Jun 20) Half-Life. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554498 on 2025 Feb 14.
[3] National Library of Medicine. (n.d.) Chapter 2 – How Stimulants Affect the Brain and Behavior. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK576548 on 2025 Feb 14.
[4] National Library of Medicine. (2013) Benzodiazepine Pharmacology and Central Nervous System-Mediated Effects. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3684331 on 2025 Feb 14.
[5] National Library of Medicine. (2016 May 1) Opioid Half-Lives and Hemlines: The Long and Short of Fashion. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4439340 on 2025 Feb 14.
[6] National Library of Medicine. (202 Nov) Mechanism of Action: Pharmacokinetics of Cannabis. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8803256 on 12025 Feb 14.
[7] Cleveland Clinic. (2021 Dec 3) How Long Does Alcohol Stay in Your System? Retrieved from https://health.clevelandclinic.org/how-long-does-alcohol-stay-in-your-system on 2025 Feb 14.
[8] Merck Manual/ (2024 Nov) Drug Elimination. Retrieved from https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/drugs/administration-and-kinetics-of-drugs/drug-elimination on 2025 Feb 14.
[9] National Library of Medicine. (2004 Ap 26) Detection Times of Drugs of Abuse in Blood, Urine, and Oral Fluid. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15228165/ on 2025 Feb 14.
[10] MedlinePlus. (2024 Jan 3) Alcohol. Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov/alcohol.html on 2025 Feb 14.
[11] Drugs.com. (2023 Aug 23) Adderall. Retrieved from https://www.drugs.com/adderall.html on 2025 Feb 14.
[12] U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration. (n.d.) Methamphetamine. Retrieved from https://www.dea.gov/factsheets/methamphetamine on 2025 Feb 14.
[13] Cleveland Clinic. ( 2022 June 14) Barbituates. Retrieved from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/23271-barbiturates on 2025 Feb 14.
[14] Stat Pearls. (2024 Jan 30) Benzodiazepines. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470159/ on 2025 Feb 14.
[15] National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. (2019 Nov) Cannabis (Marijuana) and Cannabinoids: What You Need to Know. Retrieved from https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/cannabis-marijuana-and-cannabinoids-what-you-need-to-know on 2025 Feb 14.
[16] U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration. (n.d.) Cocaine. Retrieved from https://www.dea.gov/factsheets/cocaine on 2025 14 Feb.
[17] MedlinePlus. (2024 Apr 20) Codeine. Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a682065.html on 2025 Feb 14.
[18] U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration. (n.d.) Morphine. Retrieved from https://www.dea.gov/factsheets/morphine on (n.d.)
[19] Heroin. Retrieved from https://www.dea.gov/factsheets/heroin on 2025 Feb 14.
2025 Feb 14.
[20] U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration. (2023 Apr) Phencyclidine. Retrieved from https://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/drug_chem_info/pcp.pdf on 2025 Feb 14.
[21] National Institute on Drug Abuse. (2022 Jan) Naloxone Drug Facts. Retrieved from https://nida.nih.gov/publications/drugfacts/naloxone on 2025 Feb 14.
[22] U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2018 Sep 27) Drugs of Abuse Home Use Test. Retrieved from https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/drugs-abuse-tests/drugs-abuse-home-use-test on 2025 Feb 14.
[23] Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). (n.d.) Products for Subverting Drug Tests. Retrieved from https://www.samhsa.gov/sites/default/files/donovan-dtab-products-suborn-drug-tests-dtab-sept-2014.pdf on 2025 Feb 14.
[24] John Hopkins Medicine. (n.d.) Detoxing Your Liver: Fact Versus Fiction. Retrieved from https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/detoxing-your-liver-fact-versus-fiction on 2025 Feb 14.
[25] National Library of Medicine. (n.d.) Detoxification and Substance Abuse Treatment. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK64119/ on 2025 Feb 14.
[26] National Institute of Mental Health. (n.d.) Substance Use and Co-Occurring Mental Disorders. Retrieved from https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/substance-use-and-mental-health on 2025 Feb 14.
[27] National Institute on Drug Abuse. (202 Jul) Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction. Retrieved from https://nida.nih.gov/publications/drugs-brains-behavior-science-addiction/drugs-brain on 2025 Feb 15.
[28] State of Wyoming Legislature. (2020) Substance Use Disorder Defined by NIDA. Retrieved from https://wyoleg.gov/InterimCommittee/2020/10-20201105Handoutfor6JtMHSACraig11.4.20.pdf on 2025 Feb 15.